Penstemon digitalis, foxglove beardtongue, is a native perennial herbaceous plant that blooms when most of the spring flowers are done and the summer flowers are not up yet. Its bright white flowers that adorn upright tall stalks make them easy to spot in fields and edges. Common names include foxglove penstemon, smooth white penstemon, and white beardtongue
Flowers
Inflorescence/Flower cluster:
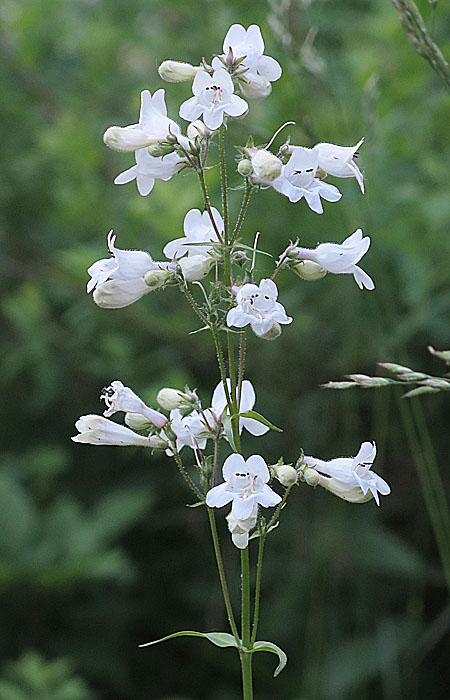 In Penstemon digitalis, the flower cluster occurs in the upper part of a long unbranched plant stem. All the flowers come from branches off of the main stem.
In Penstemon digitalis, the flower cluster occurs in the upper part of a long unbranched plant stem. All the flowers come from branches off of the main stem.
On the upper part of the main stem, at each node there are two opposite leaves where 2 flower stalks arise, one at each of the axils (where stem-leaf meets). The growth pattern is termed 'raceme'. Each of the flower stalks is also a raceme since it has similar nodes with flower stalks. Together the growth pattern is termed 'panicle'. However, the final flower groups are frequently termed 'cyme' meaning that last stem ends in single terminal flower and other flowers are lateral.
In the photo at the left, this can easily seen starting at the bottom of the stem. The leaves are opposite and a long flower stalk grows upward at each of leaf axils.
If you look carefully up the main stalk, there are two more of these leaf nodes with flower stalks coming from them. As you go up, the flower stems are shorter.
If you look at the flower stalks from these main leaf nodes, you will see the same branching pattern and they terminate with a few stemmed flowers.
Individual Flower:
The flowers are white to pale pink and about 1 inch long. The tubular corolla flares into 5 lobes; the upper lip has two lobes and the lower lip has 3 larger lobes. The corolla has some purple streaks on its inner lower surface which act as nectar guides leading the pollinator deep into the base of the flower. The nectaries are located at the base of the stamen filaments. The upper side of the corolla has a ridge and there are none on the lower surface.
The calyx has 5 short narrow pointed sepals that spread out and are reflexive. The corolla, calyx, buds and nearby flower stalks are covered with glandular hairs.
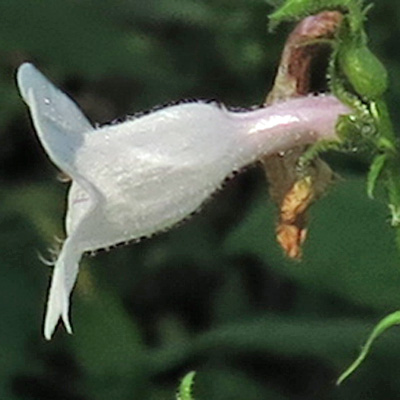
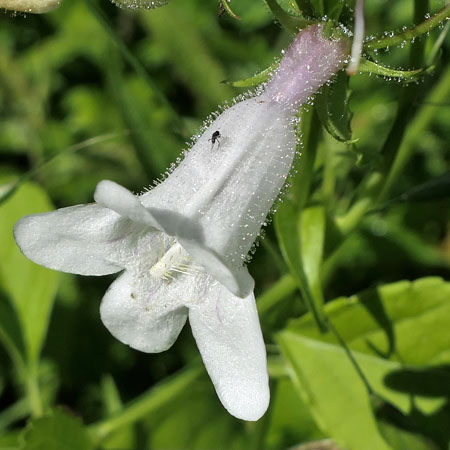
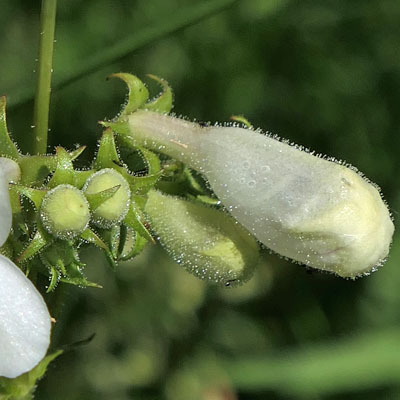
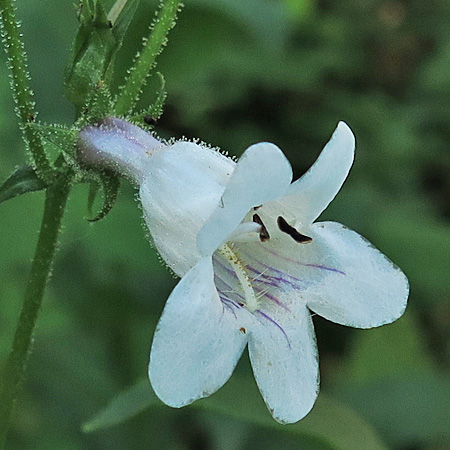



Into the mouth of the flower:
The long white structure just above the middle lower lip extending almost to the end of the corolla is a non-fertile stamen/staminoide. This conspicuous staminoide is covered along its length with long brown to white/yellow hairs. This gives the pentemons the common name beardtongue. The inner surface of the corolla has a few long white hairs too
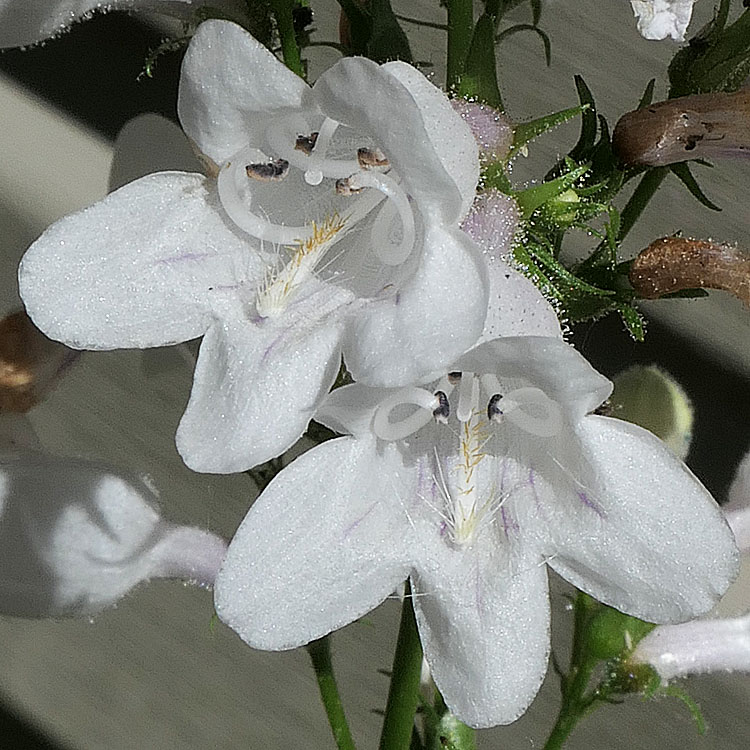
In the throat of the corolla in addition to the staminoide, are 1 pistil and 4 fertile stamens as 2 pairs.
The style of the pistil hugs the upper surface of the tube and extends to the corolla opening.
The filaments of the fertile stamens, instead of extending straight out, curl around hugging the inner surface so that anthers of each pair come together near the top, one pair close to the opening and the second pair behind. The anthers are dark brown.
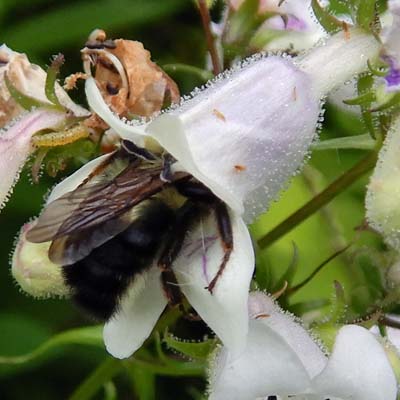
P. digitalis, like many other plants, exhibits the strategy of protandry to promote cross pollination and reduce self pollination. The male reproductive parts mature before the female parts. More specifically, the pollen is ready before the stigma is receptive. P. digitalis provides nectar and pollen for its pollinators which include bee, moths and butterflies .
By having the stamen filaments curl around, a large space is created for pollinating insects. In this image, the flower is in the male phase. The stigma is barely seen just below the upper lips.
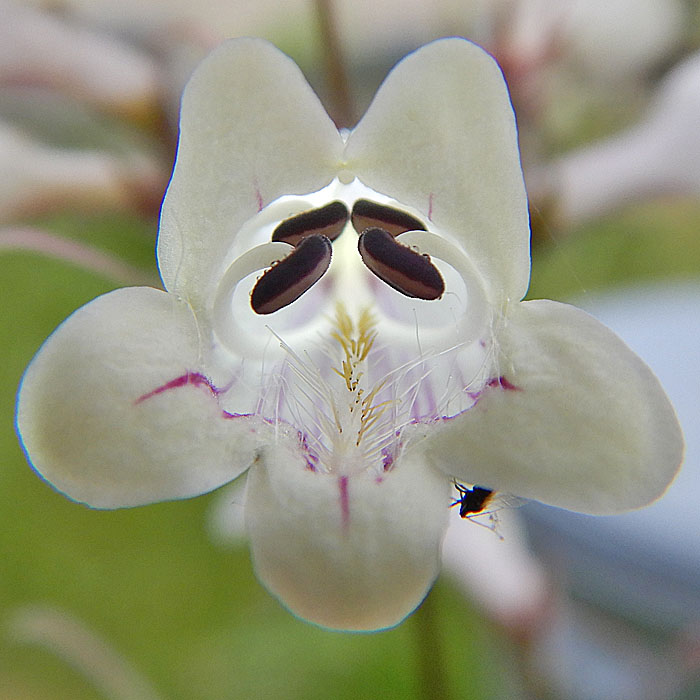

In this image, the flower is in the female phase. The pistil style has lengthened and bends downward in front into the position where the anthers were previously. The anthers have moved aside. Then the insect receives the pollen and releases pollen in the same way but to different plants.
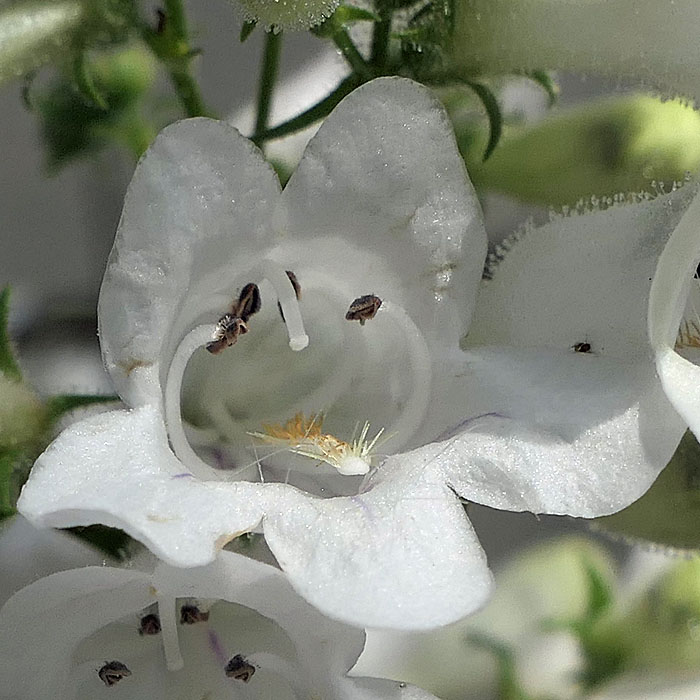

Hairs on the lower inner surface of the corolla can easily be seen in this photo.

Bee stuffed penstemon wrap.

Dissected Flower & Nectary
A flower was dissected and the staminoide and some of the petals were removed. The green ovary can be seen in the narrow part of the corolla. Also seen are the bases of the stamen filament which has the nectaries.

This is a microphotograph of the base of a stamen filament in the narrow part of the corolla.. The shiny yellow area is a nectary.

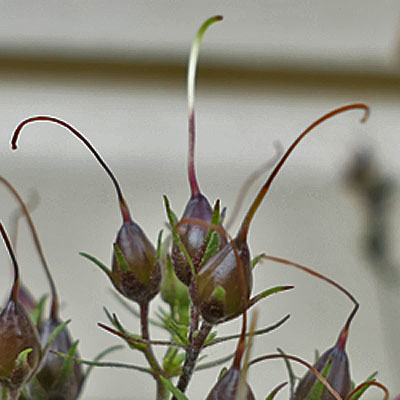
Fruit

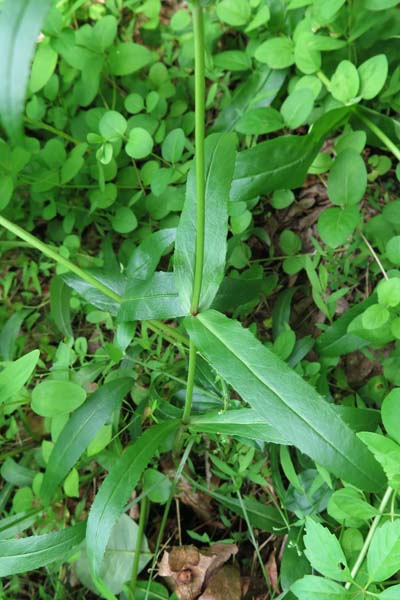
Plant and Leaves
 The plant grows to about 3 to 4 ft. The plant stalk does not branch until it is producing the inflorescence. The stem is smooth/hairless. In the flower cluster, some of the stalks may be hairy. Several tall stems may come from a single large plant.
The plant grows to about 3 to 4 ft. The plant stalk does not branch until it is producing the inflorescence. The stem is smooth/hairless. In the flower cluster, some of the stalks may be hairy. Several tall stems may come from a single large plant.
Underground the plant has rhizomes which are stems that grow horizontally and can send up shoots and send down roots for a new plant. Several plants can be connected underground.
The plant has both basal & cauline leaves. Before blooming, the plant has rosettes of basal leaves. These leaves may over-winter. These leaves have petioles (leaf stalks) and the leaf shapes are variable.

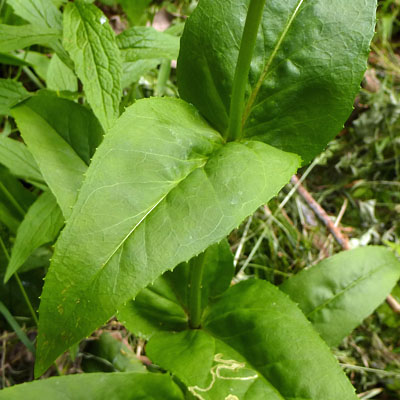
The cauline leaves (stem leaves) are sessile.

These cauline leaves are on a larger plant.

Habitat
Habitats include open areas and woodland borders.
Text by Millie Ling and all photos by Hubert & Millie Ling. Photos: flowers - June, in cultivation, various parks/preserves in central and northern NJ. They are fairly common
Cultivation
The cultivation material below is courtesy of
Jersey Friendly Yards searchable plant database: Penstemon digitalis
Bloom Times: Spring, Late Spring to Early Summer
Hardiness Zone: 6a, 6b, 7a, 7b
Soil Type: Loam, Organic, Sandy, Clay
Soil Moisture: Dry, Moist, Wet
Drought Tolerance: Medium
Soil pH: Acidic, Slightly Acidic, Neutral, Slightly Alkaline
Salt Tolerance: Medium
Optimal Light: Full Sun
Light Range: Full Sun, Partial Shade
Size: 3-5 ft tall, 1-2ft spread
Growth Rate: Medium
Deer Resistance: None
Additional information
Additional information / references:
- The USDA website shows Penstemon digitalis distribution in the US and other information: https://plants.sc.egov.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=PEDI
- Nectary size is a pollination syndrome trait in Penstemon - nectaries on stamen filament base: https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/nph.15769
- Mary Ann Borge - pollination https://the-natural-web.org/2016/06/26/white-beardtongue-for-pollinators/
- Arkansas Native Plant Society - Know your Native - good information and photos: https://anps.org/2018/06/12/know-your-natives-foxglove-beardtongue/
- Missouriplants- good information and photos: http://www.missouriplants.com/Penstemon_digitalis_page.html
- Jersey-Friendly Yards - great gardening information: https://www.jerseyyards.org/plant/penstemon-digitalis/